Steganography is concealing code inside image files that appear normal when opened in an image viewer.
In the case of Worok, Avast says the threat actors used a technique called "least significant bit (LSB) encoding," which embeds small chunks of the malicious code in the least important bits of the image's pixels.
 |
| LSB on image pixels Source: Avast |
The first payload extracted from those bits by PNGLoader is a PowerShell script that neither ESET nor Avast could retrieve.
The second payload hiding in the PNG files is a custom .NET C# info-stealer (DropBoxControl) that abuses the DropBox file hosting service for C2 communication, file exfiltration, and more.
The PNG image containing the second payload is the following:
 |
| A PNG image file containing the info-stealer Source: Avast |
DropBox abuse
The 'DropBoxControl' malware uses an actor-controlled DropBox account to receive data and commands or upload files from the compromised machine.
The commands are stored in encrypted files on the threat actor's DropBox repository that the malware accesses periodically to retrieve pending actions.
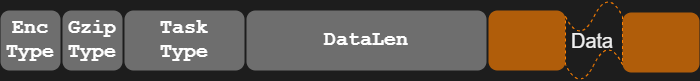
Source: Avast
The supported commands are the following:
- Run "cmd /c" with the given parameters
- Launch an executable with given parameters
- Download data from DropBox to the device
- Upload data from the device to DropBox
- Delete data on the victim's system
- Rename data on the victim’s system
- Exfiltrate file info from a defined directory
- Set a new directory for the backdoor
- Exfiltrate system information
- Update the backdoor’s configuration
These functions indicate that Worok is a cyberespionage group interested in stealthy data exfiltration, lateral movement, and spying on the infected device.
Avast comments that the tools sampled from Worok attacks aren't circulating in the wild, so they're likely used exclusively by the threat group.

